Introduction
Cancer treatment has changed dramatically in recent years. One of the biggest breakthroughs is CAR T-cell therapy a form of immunotherapy that uses a patient’s own immune system to fight cancer in a powerful and targeted way. It is already saving lives in patients with certain blood cancers, especially those who have failed multiple other treatments.
Let’s explore what CAR T-cell therapy is, how it works, who it helps, and the drugs currently approved under this treatment approach.
Need affordable cancer treatment in Chennai then book a appointment with Jus’Onco Clinic Today
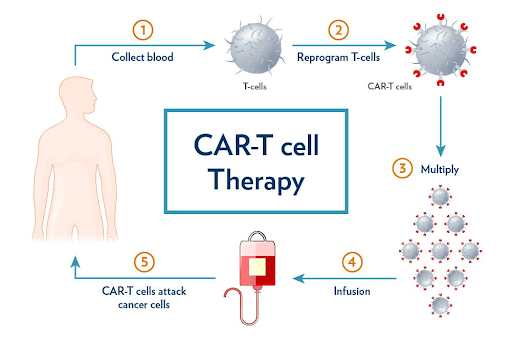
What Is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy stands for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy.
It’s a type of personalized immunotherapy that uses a patient’s own immune system to kill cancer cells.
Here’s how it works:
- Collection – Doctors take T-cells (a type of white blood cell) from the patient’s blood.
- Reprogramming – In a lab, scientists add special receptors (CARs) to the T-cells to help them recognize cancer cells.
- Multiplication – These modified T-cells are grown in large numbers.
- Infusion – The CAR T-cells are put back into the patient’s bloodstream, where they hunt down and destroy cancer cells.
It’s like teaching your body’s soldiers how to identify and destroy the enemy (cancer).
Which Cancers Can Be Treated with CAR T-Cell Therapy?
Currently, CAR T-cell therapy is used mainly for blood cancers, especially when the disease is relapsed or resistant to other treatments:
- B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) – mostly in children and young adults
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
- Follicular Lymphoma
- Multiple Myeloma
In the future, it may also be used for solid tumors like brain, lung, or ovarian cancer — research is ongoing.
Benefits of CAR T-Cell Therapy
- High remission rates: Many patients go into complete remission, even after failing other treatments.
- One-time treatment: It is often given just once, unlike chemotherapy cycles.
- Personalized: It uses the patient’s own cells, reducing the risk of rejection.
- Growing research: Trials are exploring new targets and new cancers.
Get guidance on accessing CAR T-cell therapy, connect with clinical trials, and explore affordable treatment options at Jus’Onco Clinic, Chennai.
Approved CAR T-Cell Therapy Drugs
Below are the key CAR T-cell drugs approved as of 2025. These are available in the US, EU, and some parts of Asia, though access in India is still limited.Axicabtagene Ciloleucel
Brand name: Yescarta Cancer types:-
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma
Brexucabtagene Autoleucel
Brand name: Tecartus Cancer types:-
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel
Brand name: Carvykti Cancer types:-
- Relapsed/refractory Multiple Myeloma
Idecabtagene Vicleucel
Brand name: Abecma Cancer types:-
- Multiple Myeloma after failure of 4+ previous treatments
Lisocabtagene Maraleucel
Brand name: Breyanzi Cancer types:-
- Relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas
Tisagenlecleucel
Brand name: Kymriah Cancer types:-
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in children and young adults
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) in adults
IMPACT-CAR19 – MADE IN INDIA
A Made-in-India CAR T-Cell Therapy Breakthrough What is it? IMPACT-CAR19 is India’s first indigenous CAR T-cell therapy, developed to treat blood cancers such as Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and B-cell lymphomas. It targets CD19, a protein found on many cancerous B cells. Who developed it? It is a collaborative project between:-
- Tata Memorial Centre (India’s leading cancer hospital)
- IIT Bombay (Indian Institute of Technology Bombay)
- ImmunoACT, a start-up founded from this collaboration This effort represents India’s bold step into advanced, home-grown cancer immunotherapy.
-
- The first phase of human trials began in 2022.
- Early results have been promising, with good safety profiles and cancer response rates.
- Now entering wider trials to seek approvals for broader clinical use.
-
- Only in select clinical trial centers, mainly Tata Memorial Hospital (Mumbai)
- Not yet approved for commercial use
- Expansion to more centers is expected after trial success and regulatory approval
How Is CAR T-Cell Therapy Given?
The treatment process typically takes 3–4 weeks and includes:- Leukapheresis – Patient Blood is taken and T-cells are collected.
- Cell Engineering – T-cells are modified and grown in the lab.
- Chemotherapy (Lymphodepletion) – Prepares the patient body for CAR T-cells.
- CAR T-cell Infusion – The modified cells are returned to the patient body.
- Monitoring – For side effects like CRS (Cytokine Release Syndrome) and infections
Side Effects of CAR T-Cell Therapy
Though powerful, CAR T therapy is not without side effects:- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
- Body’s immune system reacts strongly.
- Fever, low blood pressure, and organ stress.
- Can be managed with steroids or tocilizumab.
- Neurological Toxicity
- Confusion, seizures, or difficulty speaking.
- Usually temporary but needs careful monitoring.
- Low Blood Counts
- Increased risk of infection or bleeding.
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Common after infusion, usually improves with time.
Get guidance on accessing CAR T-cell therapy, connect with clinical trials, and explore affordable treatment options at Jus’Onco Clinic, Chennai.
What Is the Cost of CAR T Therapy in India?
As of 2025:
Imported therapies: ₹3.5 to ₹6 crore
Indian initiatives (IMPACT-CAR19) : ₹25–40 lakh
Challenges:
- Complex lab setup
- Manufacturing time (2–4 weeks)
- Trained hospital teams required
Financial Assistance
Crowd funding
Where Can You Get CAR T-Cell Therapy in India?
As of mid-2025, CAR T therapy in India is being offered in trial or compassionate settings at:
- Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai
- AIIMS Delhi
- Immuno ACT Biotech (spin-off from IIT Bombay)
These centers are working with Indian biotech companies to develop affordable, indigenous CAR T products.
Future of CAR T-Cell Therapy
- Solid Tumors
While CAR T has worked best in blood cancers, trials are exploring its use in:
- Brain tumors (glioblastoma)
- Pancreatic cancer
- Lung and breast cancers
- Universal or Off-the-Shelf CAR T-Cells
- These cells are made from healthy donors.
- Ready-to-use, shorter wait time.
- Still being tested.
- Dual-targeted CARs
- Can recognize two cancer proteins to prevent escape and relapse.
- Combination with Other Drugs
- CAR T with checkpoint inhibitors or kinase inhibitors to improve response.
Final Message
CAR T-cell therapy is one of the biggest breakthroughs in modern cancer care. It offers real hope for patients who have run out of options. While still expensive and limited in availability, things are changing — especially in India.
At Jus’Onco, we are committed to guiding patients through these new treatments. From referrals to top hospitals to connecting with clinical trials and support groups, we help every patient access the care they deserve.
Together, let’s bring cutting-edge cancer care closer to home.
Get guidance on accessing CAR T-cell therapy, connect with clinical trials, and explore affordable treatment options at Jus’Onco Clinic, Chennai.
FAQ
1. What is CAR T-cell therapy, and how does it work?
CAR T-cell therapy is a personalized immunotherapy that reprograms a patient’s own T-cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells. It is highly effective in certain blood cancers.
2. Which cancers can CAR T-cell therapy treat?
Currently, it’s approved for blood cancers like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL), Mantle Cell Lymphoma, Follicular Lymphoma, and Multiple Myeloma. Trials are ongoing for solid tumors.
3. How much does CAR T-cell therapy cost in India?
Imported CAR T therapies cost ₹3.5–₹6 crore. India’s first indigenous therapy, IMPACT-CAR19, is expected to cost ₹25–40 lakh—nearly 90% less.
4. Where is CAR T-cell therapy available in India?
As of 2025, CAR T therapy is available only in select clinical trial centers like Tata Memorial Centre (Mumbai), AIIMS Delhi, and through ImmunoACT Biotech.
5. What are the main side effects of CAR T-cell therapy?
Side effects may include cytokine release syndrome (fever, low BP), neurological issues (confusion, seizures), low blood counts, and fatigue. Most are manageable with proper hospital monitoring.
