Chemotherapy Costs in Chennai: What to Expect & How to Estimate Expenses
by jusonco.com | Aug 31, 2025 | Blogs
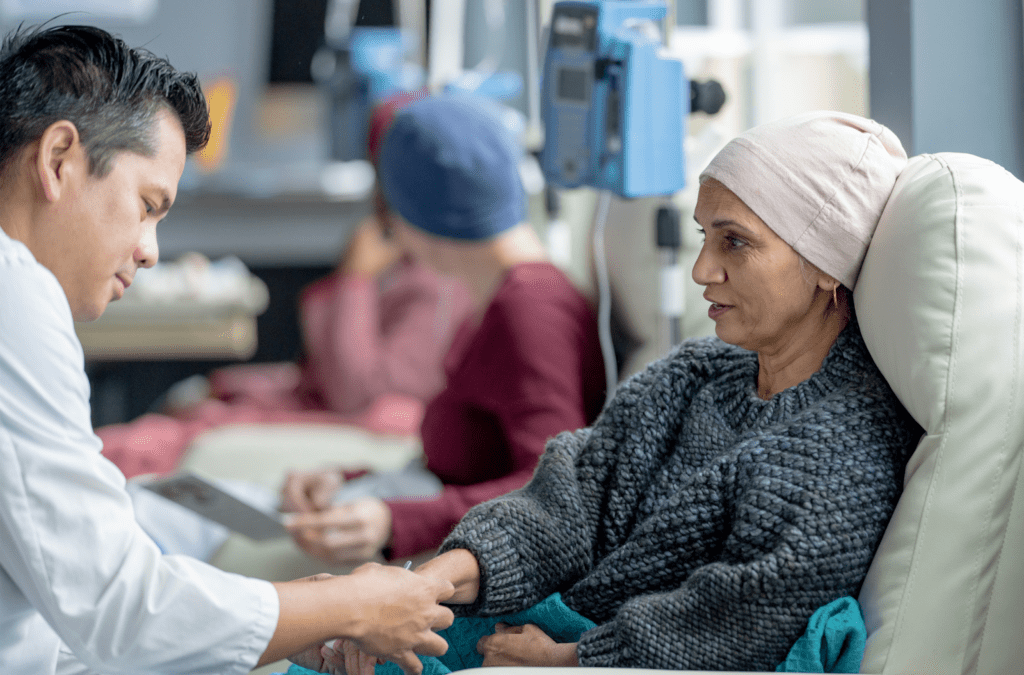
Chemotherapy is one of the most commonly used treatments for cancer. It helps destroy cancer cells, shrink tumors, and increase the chances of cure or long-term control. But one of the biggest challenges faced by patients and families in cities like Chennai is understanding and managing the cost of chemotherapy.
Let’s explore what goes into chemotherapy expenses, how you can plan, and how Jus’Onco helps make cancer care more affordable.
For best chemotherapy treatment in chennai contact Jus’Onco Today!
What is Chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy refers to the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It can be used alone or along with surgery, radiation, or targeted therapy.
- Chemotherapy is usually given in cycles and may continue for several months.
- Some regimens involve weekly visits, while others are spaced every 2–3 weeks.
- Each cycle includes the treatment itself followed by a period of rest and recovery.
The total number of cycles varies based on cancer type, patient’s response, and side effect tolerance.
What is the Average Cost of Chemotherapy in Chennai?
The cost of chemotherapy varies depending on many factors. On average:
- Cost per cycle: ₹5,000 to ₹40,000
- Doctor & Day-care fees: ₹2,000 to ₹10,000 per visit
- Total treatment cost: ₹50,000 to ₹5,00,000+ depending on cycles and drug type
Factors influencing cost include:
- Type of cancer
- Hospital choice (government, private, or day-care centers like Jus’Onco)
- Brand vs. generic drugs
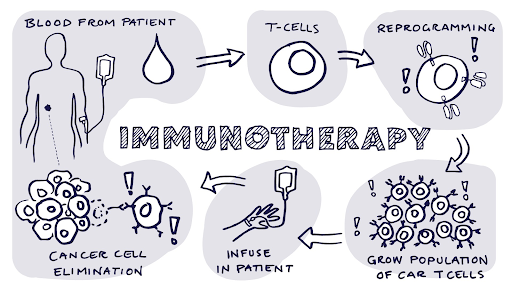
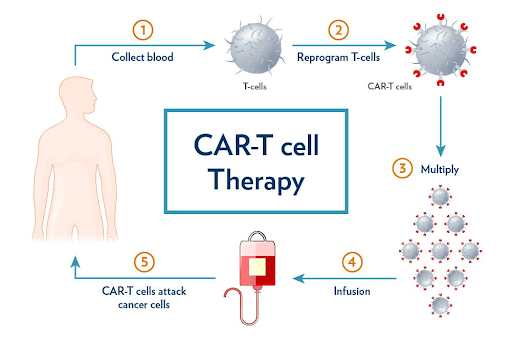
Targeted therapy or immunotherapy options
Start affordable cancer treatment in Chennai with Jus’Onco today.
Factors That Influence Chemotherapy Cost
1. Type of Cancer and Number of Cycles
Aggressive cancers may require more cycles, increasing the overall expense.
2. Type of Drugs Used
Newer targeted therapies and immunotherapies can be significantly more expensive.
3. Hospital Type
- Government hospitals: Often free or subsidized.
- Private hospitals: Higher charges.
- Day-care centers (Jus’Onco): Affordable expert-led care.
4. Oral vs. Intravenous (IV) Chemotherapy
- Oral tablets reduce hospital visits.
- IV chemotherapy requires day-care or admission.
5. Monitoring Tests
Regular scans, blood tests, and consultations add to expenses.
How Jus’Onco Helps Reduce Chemotherapy Cost
At Jus’Onco Affordable Cancer Care, we make evidence-based treatment accessible without financial stress:
- Day-care based chemo → no admission charges
- Experienced oncologists → avoid unnecessary tests or overtreatment
- Affordable drug options → generic and biosimilar drugs
- Insurance support → help with paperwork and schemes
- Flexible slots → save time and travel
- Patient education → clarity on options and costs
Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Even when chemotherapy itself is affordable, patients may face additional expenses:
- Travel and accommodation
- Nutrition supplements
- Supportive medications (anti-nausea, pain relief)
- Loss of income from work breaks
- Diagnostic tests like PET/MRI scans
Planning ahead with your care team helps reduce financial stress.
Sample Cost Estimates by Cancer Type
|
Cancer Type |
Common Regimen |
Approx. Cost per Cycle |
|
Breast Cancer |
AC, CMF, Paclitaxel |
₹7,000 – ₹25,000 |
|
Colorectal Cancer |
FOLFOX, CAPOX |
₹20,000 – ₹50,000 |
|
Lung Cancer |
Carboplatin + Paclitaxel |
₹20,000 – ₹50,000 |
|
Cervical Cancer |
Cisplatin weekly + RT |
₹5,000 – ₹10,000 |
|
Lymphoma (NHL/HL) |
CHOP, ABVD |
₹10,000 – ₹40,000 |
Start affordable cancer treatment in Chennai with Jus’Onco today.
Preparing for Chemotherapy Emotionally & Financially
- Understand the full treatment plan
- Build a support system (family, friends, groups)
- Track expenses and documents carefully
- Explore insurance/government aid early
- Continue working part-time if possible

How Day-Care Chemotherapy Works at Jus’Onco
Many patients assume chemo means long hospital stays. Today, most regimens are day-care based:
Process:
- Registration and basic checks
- Blood tests reviewed for fitness
- Drugs prepared in a sterile unit
- Comfortable recliner chemo infusion
- Observation (2–6 hrs) then home
This approach reduces cost, infection risk, and hospital time.
For best chemotherapy treatment in chennai contact Jus’Onco Today!
Real-Life Example: Affordable Breast Cancer Care
A 45-year-old woman with Stage 2 breast cancer was advised 6 cycles of chemo.
- Private hospital quote: ₹2.5 lakh
- At Jus’Onco: Same regimen with WHO-approved generics at ₹72,000 total
- Insurance covered treatment, delivered in a safe, affordable day-care setting
Insurance & Government Support
Patients in Chennai can benefit from:
- Government hospitals: Free under state schemes
- CMCHIS: State-level support
- Ayushman Bharat / PM-JAY: Select hospitals
- ESI/Private Insurance: Covers chemo, though not always all drugs
Jus’Onco helps with applications and documentation.
Tips to Manage Chemotherapy Costs
- Ask for a full treatment plan and estimate
- Check for generics and biosimilars
- Explore free counseling and second opinions
- Keep all reports organized for claims
Focus on diet and lifestyle support
Final Words
Chemotherapy can be life-saving, but cost remains a worry. At Jus’Onco, we guide you with transparency, compassion, and cost-effective care.
“Don’t delay treatment due to financial stress. Together, we fight cancer with knowledge, access, and compassion.”
For affordable chemotherapy in Chennai, reach out to the Jus’Onco team today.
Start affordable cancer treatment in Chennai with Jus’Onco today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is chemotherapy painful or risky?
Chemo is usually painless. Side effects are common but manageable.
Q2. Can I continue working while on chemotherapy?
Yes, many continue light work depending on the drug and their health.
Q3. How long does one cycle take?
30 minutes to several hours, depending on the drug
Q4. Are all chemotherapy drugs covered by insurance?
Not always. Imported or new drugs may not be covered. Alternatives are available.
Q5. Can I get chemotherapy at home?
Oral drugs can be taken at home. IV chemo requires safe centers.