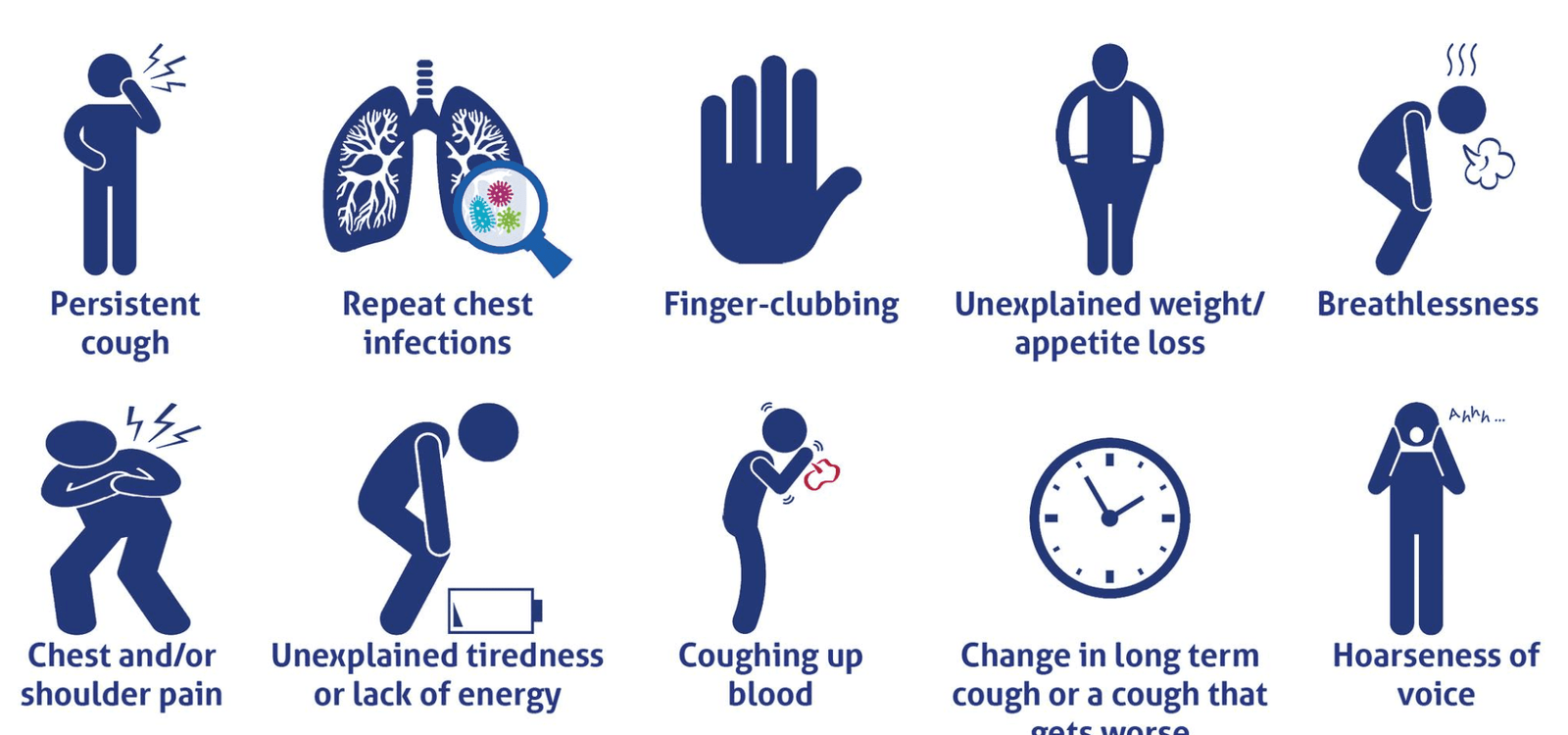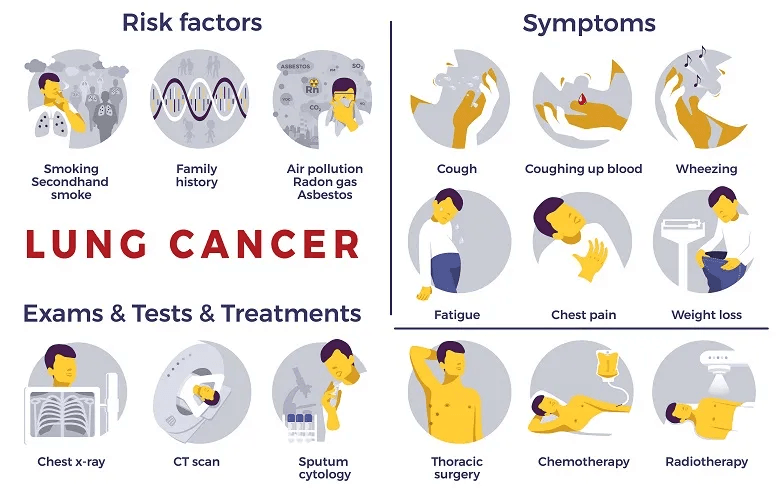
புற்றுநோய் குணமான பிறகு மீண்டும் வருமா? வேலைக்கு செல்ல முடியுமா? முழுமையான குணம் எப்போது? Jus’Onco மருத்துவ நிபுணர் விளக்கம்!
by jusonco.com | May 24, 2025 | Blogs
புற்றுநோய் என்பது சிக்கலான மற்றும் தீவிரமான சிகிச்சை தேவைப்படும் நோயாகும். உலகம் முழுவதும் கோடிக்கணக்கான மக்களை பாதிக்கும் இந்த நோய், நவீன மருத்துவ முன்னேற்றங்களால் சிறப்பான முறையில் கையாளப்படுகிறது.
ஆனாலும், புற்றுநோய் குறித்து இன்னும் பல தவறான கருத்துகள் மற்றும் கட்டுக்கதைகள் மக்கள் மத்தியில் நிலவுகின்றன. இவை, சிகிச்சைக்கு முன்பும் பின்பும் தொடர்கின்றன.
அதனால், இந்த பிழையான நம்பிக்கைகளை சீர்செய்து, உண்மையான தகவல்களை பகிர்வது அவசியமாகிறது.
Best Cancer Treatment in Chennai எனப் பேசப்படும் Jus’Onco போன்ற கிளினிக்கள், நம்பகமான சிகிச்சையை நவீன தொழில்நுட்பத்துடன் வழங்குகின்றன.

புற்றுநோய் குணமாகும் சாத்தியமா?
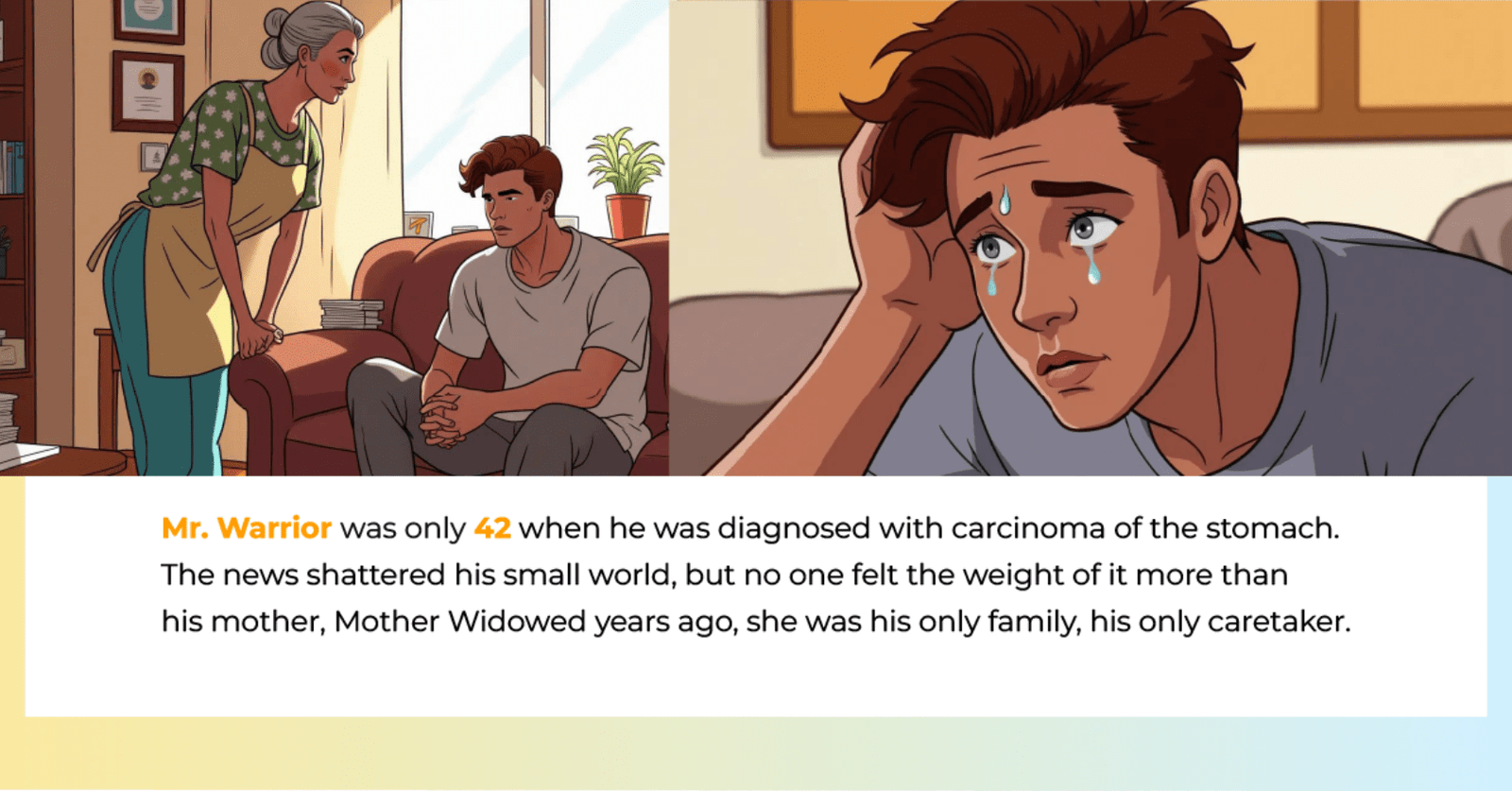
புற்றுநோய் ஆரம்ப நிலையில் கண்டறியப்படும்போது, அதைப் முழுமையாக குணப்படுத்துவதற்கான சாத்தியம் அதிகம். எனினும், “புற்றுநோய் ஒருமுறை வந்தால், மீண்டும் வரும்” என்ற பயம் பலருக்கும் இருக்கும். உண்மையில், சிகிச்சைக்குப் பிறகு தொடர்ந்து மருத்துவரின் கண்காணிப்பில் இருந்தால், மீண்டும் வருவதை நாம் எளிதாக அடையாளம் காண முடியும். Recurrence என அழைக்கிறோம்
பொதுவாக, சிகிச்சைக்குபின் 2–3 ஆண்டுகளில் புற்றுநோய் ஏற்படவில்லை என்றால், நோய் 70–80% வரை குணமடைந்துள்ளதாக கருதலாம்.
5 ஆண்டுகள் கடந்தும் நோய் திரும்பவில்லை என்றால், முழுமையாக குணமடைந்ததாக மருத்துவர்கள் உறுதி செய்வார்கள்.

வேலைக்கு திரும்ப முடியுமா?
புற்றுநோய் சிகிச்சையின் முக்கிய நோக்கம், நோயாளி மீண்டும் இயல்பான வாழ்க்கையை தொடங்குவதை உறுதிப்படுத்துவதே. சரியான சிகிச்சையும், பின்பற்ற வேண்டிய நடைமுறைகளையும் மேற்கொண்டால், நோயாளிகள் முற்றிலும் இயல்பான வாழ்க்கைக்கு திரும்ப முடியும். Jus’Onco-வில் சிகிச்சை பெற்ற பலர், தங்கள் வாழ்க்கைக்கு வலிமையாக திரும்பி, மற்றவர்களைவிட நன்கு செயல்பட்டு வருகின்றனர் என்பதும் ஒரு உண்மை.

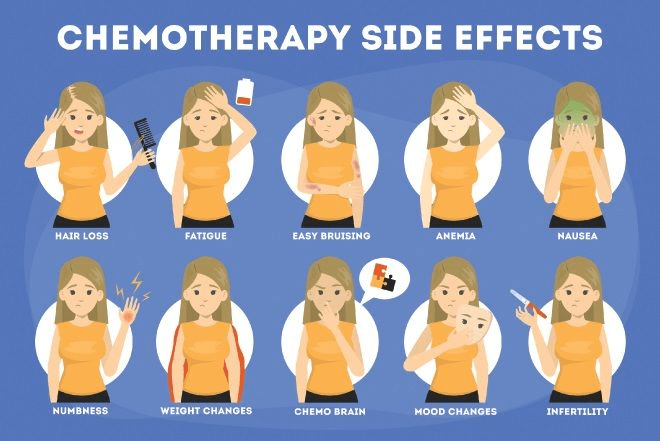
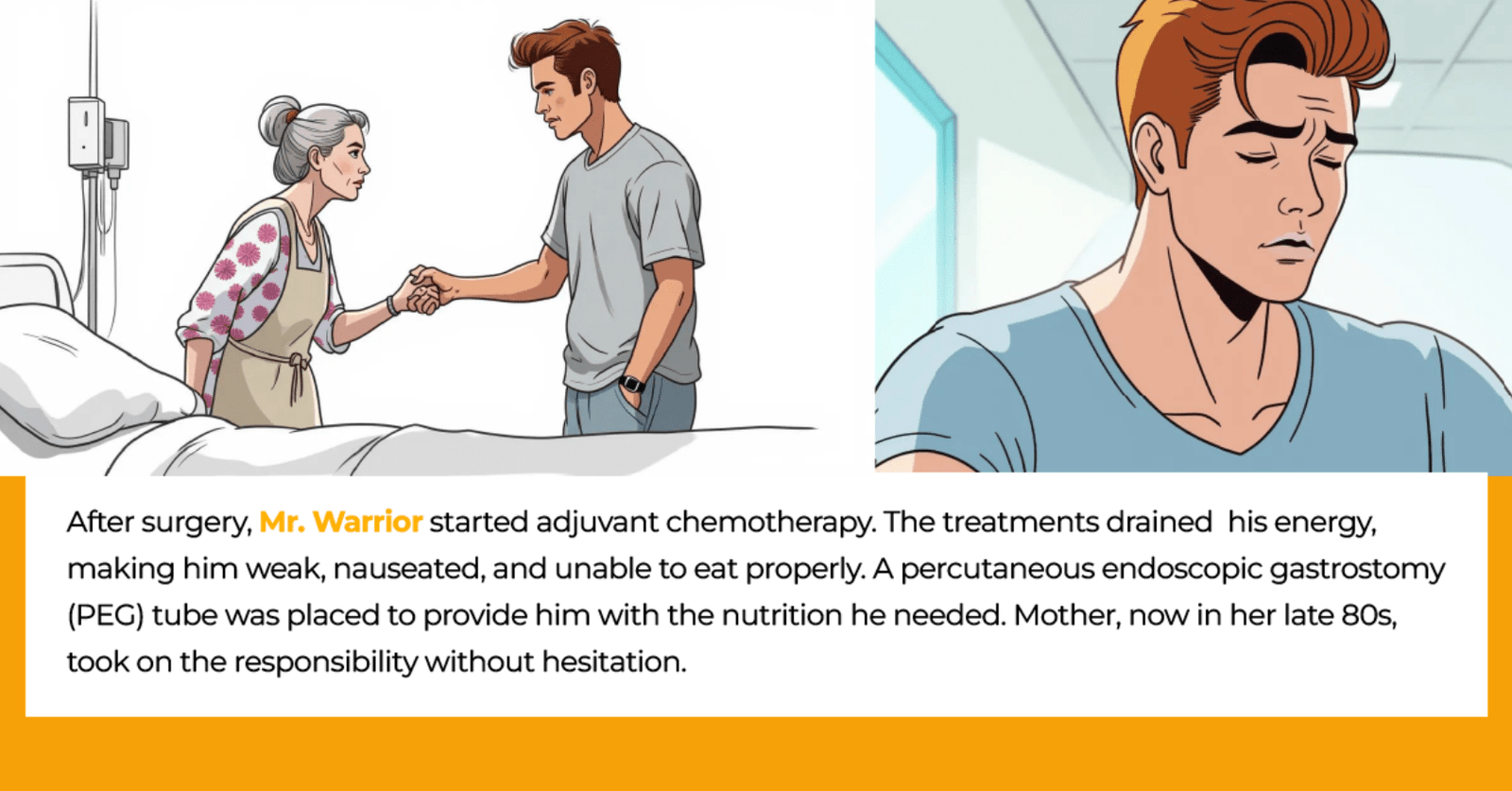
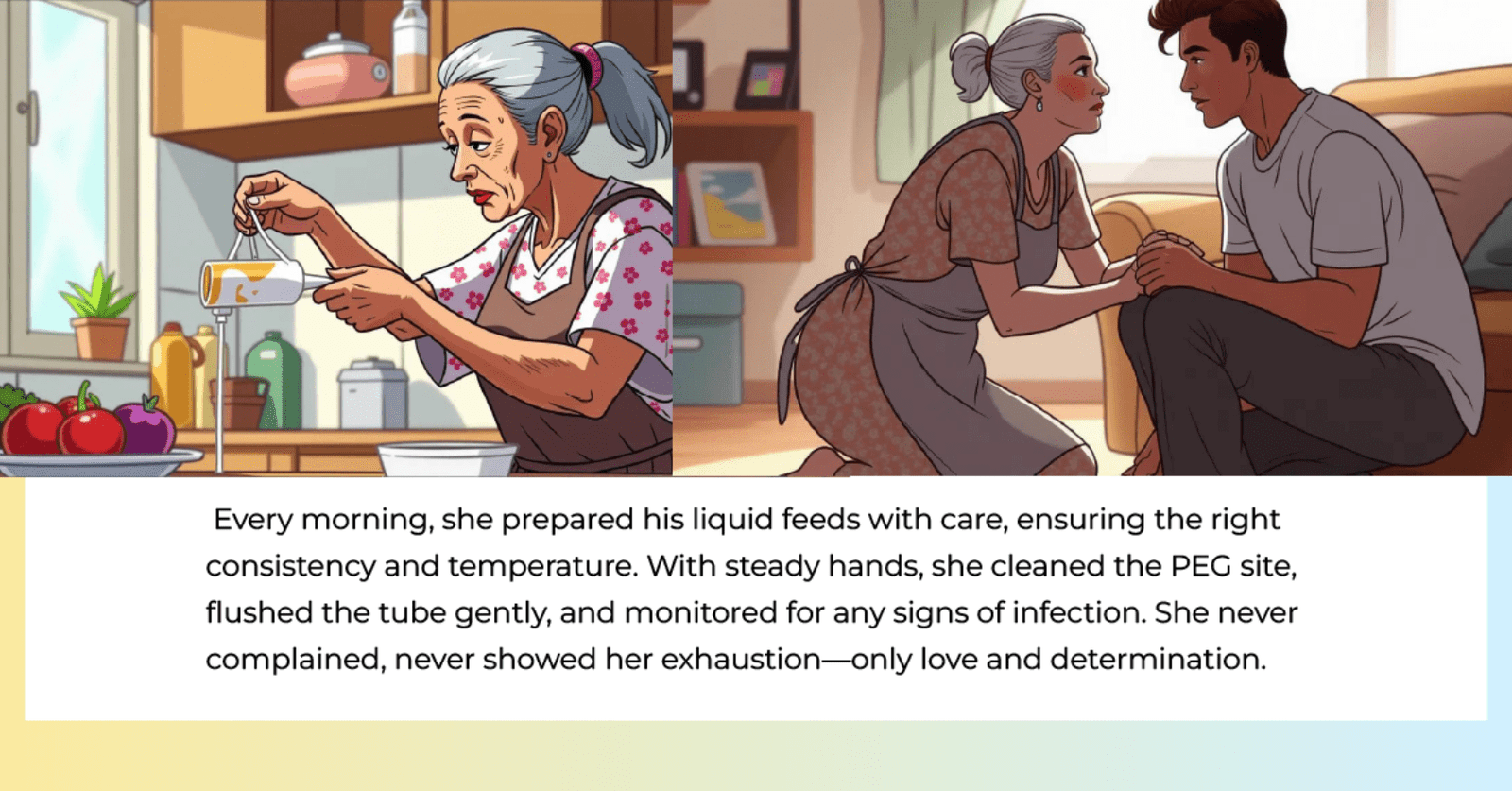
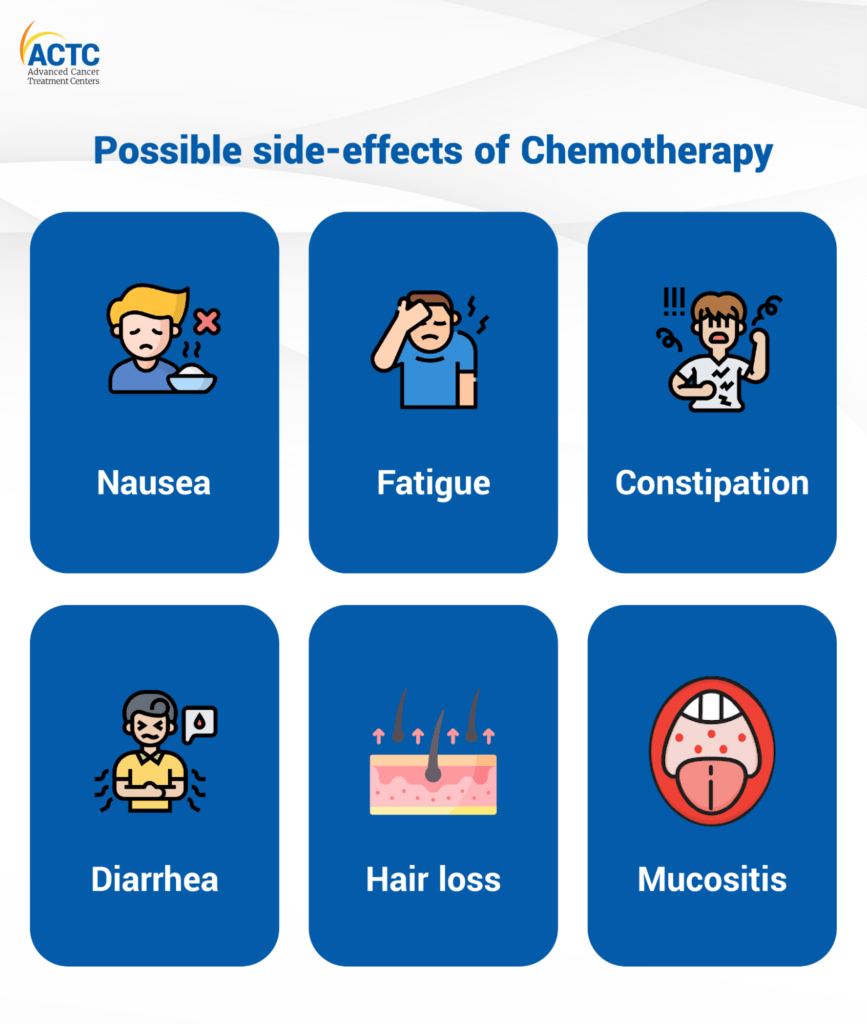
கீமோதெரபி மற்றும் பக்கவிளைவுகள் – உண்மைகள் என்ன?
இன்றைய நவீன சிகிச்சை முறைகள் – குறிப்பாக targeted chemotherapy மற்றும் minimally invasive surgery – பக்கவிளைவுகளை குறைக்கும் வகையில் வடிவமைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன.
முடி உதிர்வு, குமட்டல் போன்றவை தற்காலிகமானவை. மருந்து முடிந்த பிறகு கூந்தல் மீண்டும் வளரும்.
திருமண வாழ்க்கை மற்றும் குழந்தையடைவது சாத்தியமா?
புற்றுநோய் ஏற்பட்ட பிறகு திருமணம், கருத்தரிப்பு, குழந்தை பெற்றல் போன்றவற்றில் தடையா என்பது பலரின் கேள்வி. ஆனால், சிகிச்சைக்குப் பிறகு இயல்பு நிலைக்குத் திரும்பிய பல பெண்கள் மற்றும் ஆண்கள், திருமணம் செய்து குழந்தைகளை பெற்றிருக்கிறார்கள். பல நிறுவனங்களில், சிகிச்சைக்கு முன் விந்தணுக்கள் அல்லது கருமுட்டைகளை சேமிக்கும் வசதிகளும் வழங்கப்படுகின்றன.

இயற்கை வைத்தியம் மட்டுமே கேன்சரை குணப்படுத்துமா?
இயற்கை மருத்துவத்தின்மீது மக்கள் நம்பிக்கை கொண்டிருந்தாலும், இதுவரை அது புற்றுநோயைக் குணமாக்கும் என்ற சான்றுகள் இல்லை.
உணவுமுறைகள், வாழ்கை முறை போன்றவை பாதுகாப்புக்கே முக்கியம். ஆனால், பரிந்துரைக்கப்படும் சிகிச்சைகள் – அறுவை சிகிச்சை, கீமோதெரபி, ரேடியேஷன் – இவைதான் தற்போதைய நம்பகமான முறைகள்.

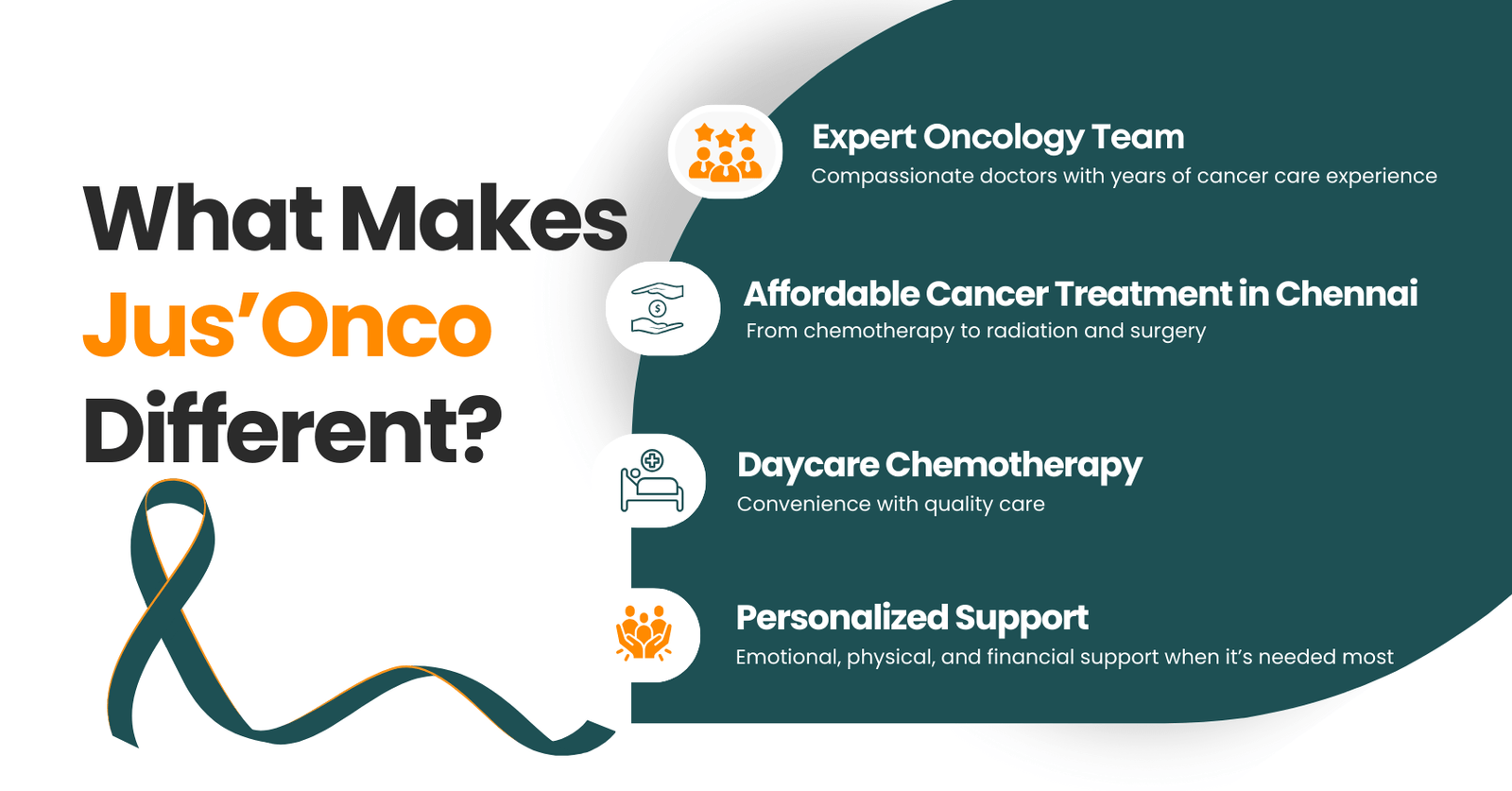
Jus’Onco – நம்பிக்கைக்குரிய புற்றுநோய் சிகிச்சை மையம்
புற்றுநோயை பற்றிய இவ்வாறான சந்தேகங்களுக்கு தெளிவான medically accurate பதில்களை Jus’Onco-வின் cancer நிபுணர்கள் வழங்கி வருகின்றனர். Jus’Onco கிளினிக்கில், best oncologist in Chennai ஆகியோர் பணியாற்றி, நோயாளிகளுக்குத் தனிப்பட்ட சிகிச்சை திட்டங்களை வகுப்பதுடன், உயர் தர மருத்துவ வசதிகளைவும் வழங்குகிறார்கள்.
மேலும், Jus’Onco:
- Affordable chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy & surgical oncology
- நோயாளிகளுக்காக, அவர்களின் வீட்டு அருகிலேயே உள்ள மருத்துவமனையில் சிகிச்சை பெறும் வசதிகள்
- இறுதிக்கட்ட புற்றுநோயாளிகளுக்காக Palliative Care சேவைகள் வழங்கி வருகின்றது.

உங்கள் புற்றுநோய் சிகிச்சை பயணத்தில் நம்பிக்கையுடனும், நவீன மருத்துவத்துடனும் Jus’Onco உங்கள் பக்கத்தில் இருக்கிறது.
We Fight together against Cancer
Join us in the fight against cancer — spreading hope, strength, and support every step of the way.